Search Results for caryopsis
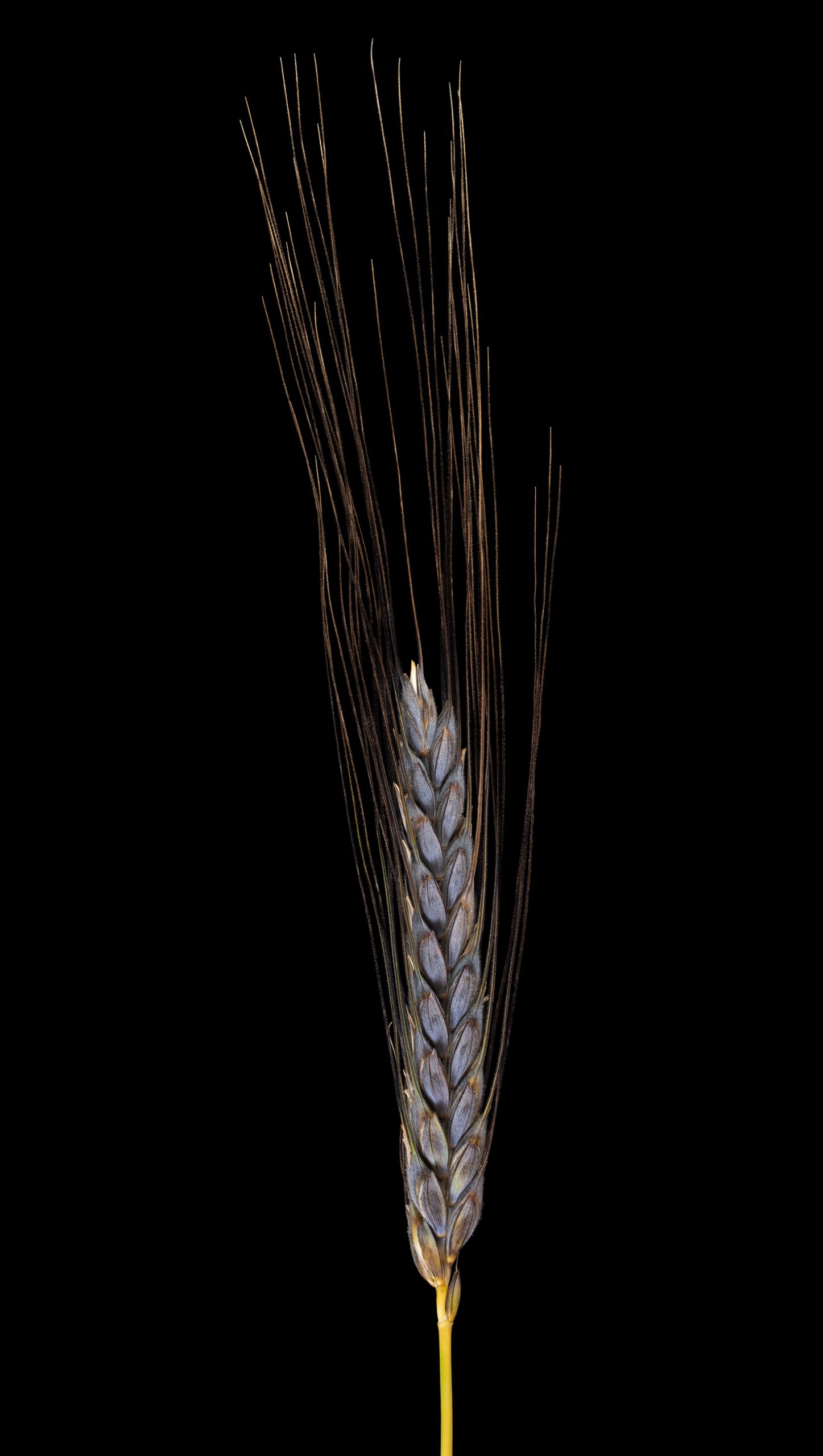
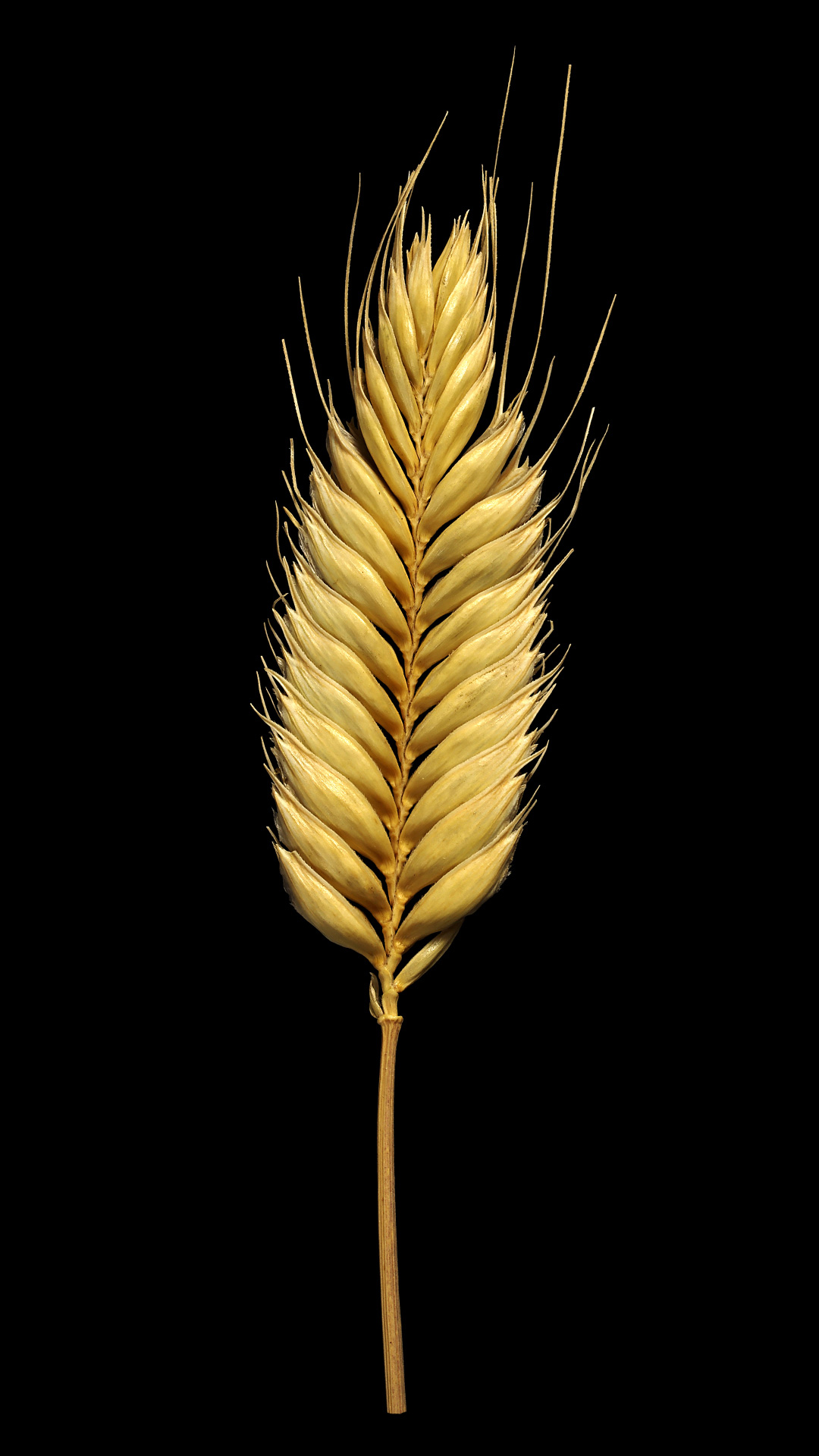
The protein (gluten) it contains is not said to have good adhesive properties, but black emmer wheat is nevertheless suitable for baking bread and pastries.
The grains are edible raw and cooked: crushed into porridge or ground into flour from which bread can finally be baked.
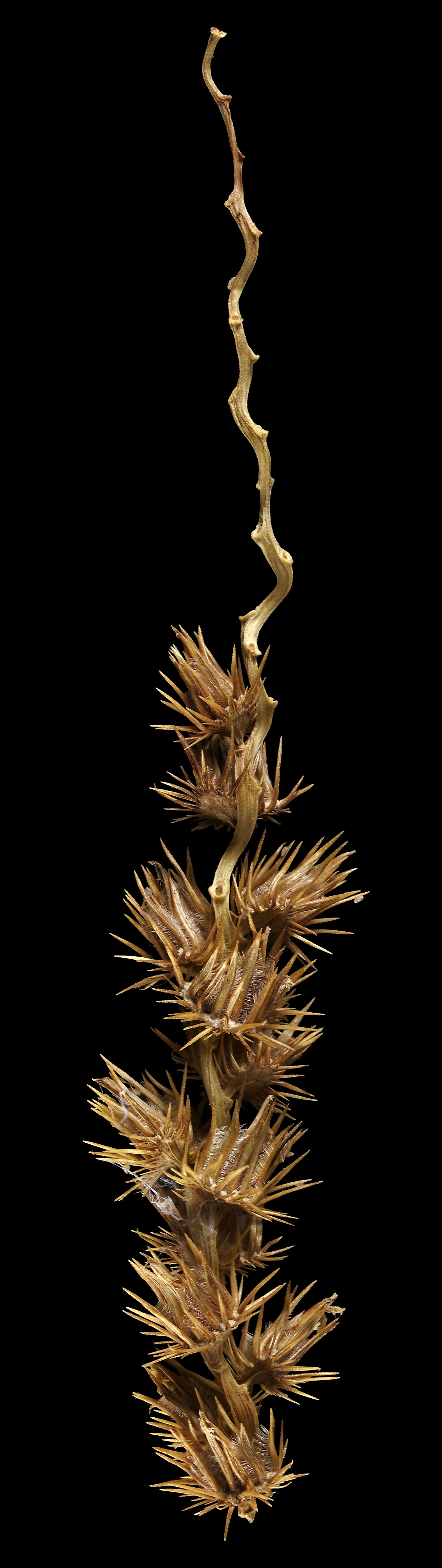
Despite its numerous uses, which are also used for medical purposes, Job’s tears are not very popular compared to other cereals. The cultivation is even declining.
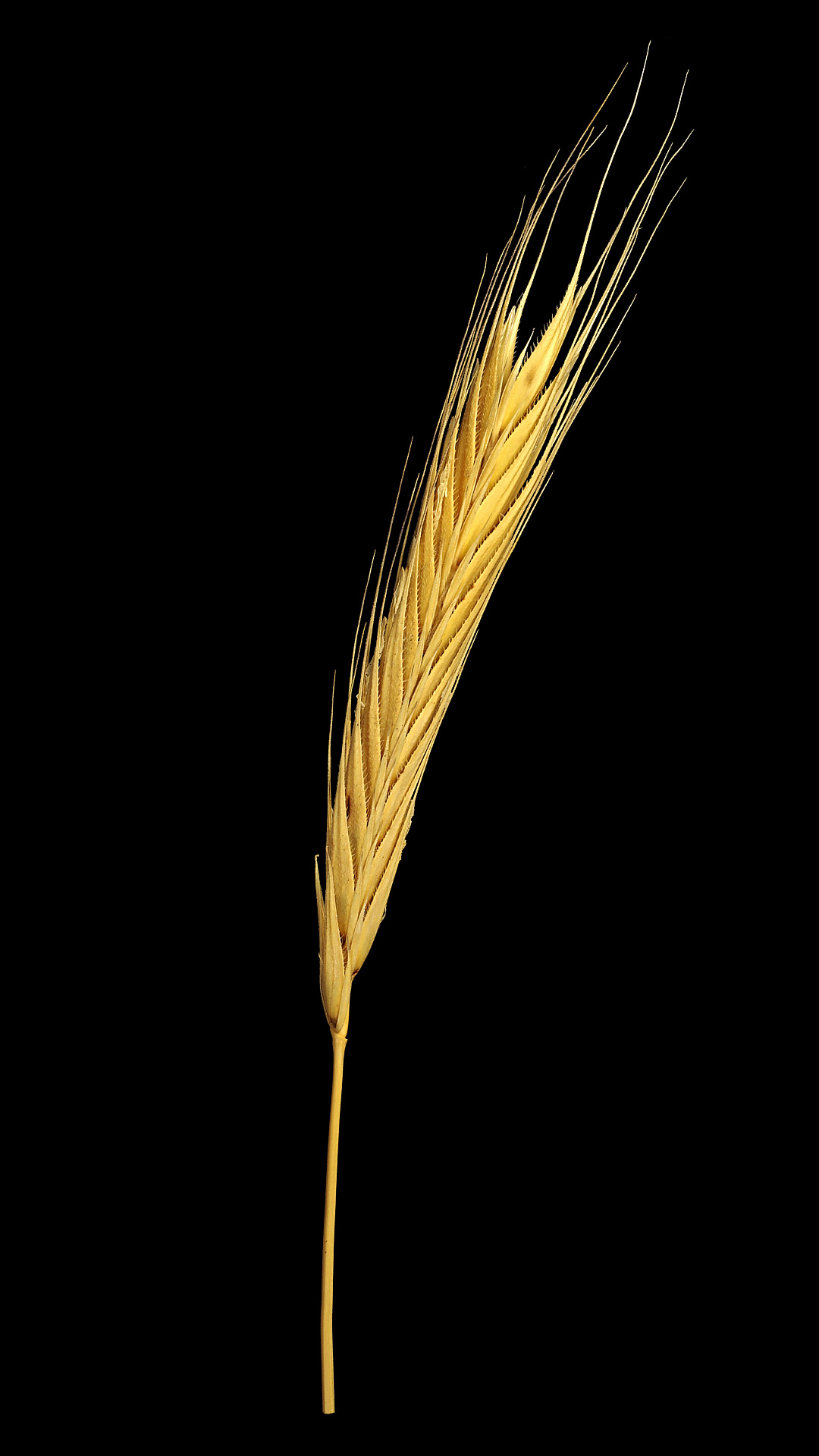
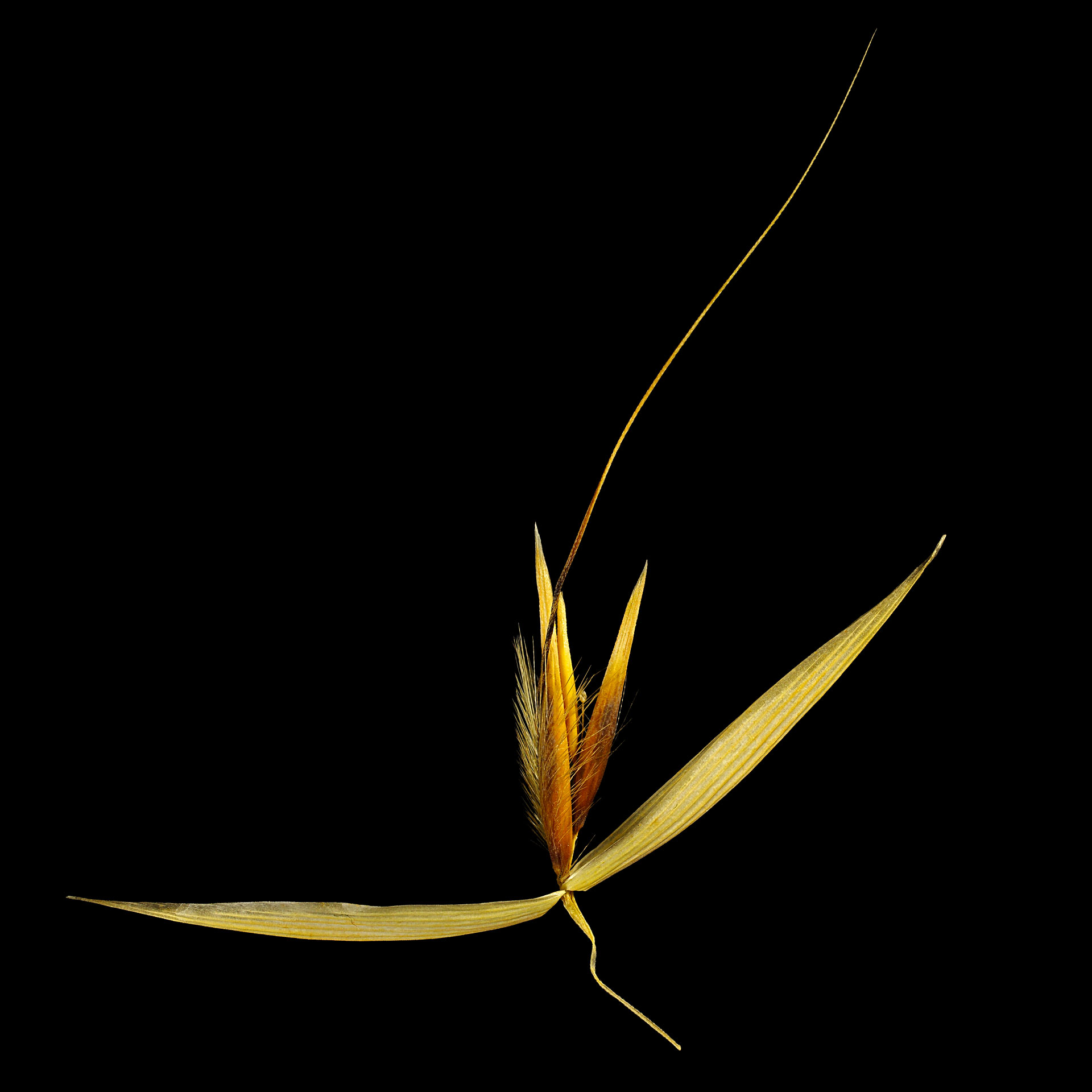
Like most wild forms, also those of rye are not particularly productive and are rarely or no longer cultivated today in contrast to the cultivated forms.
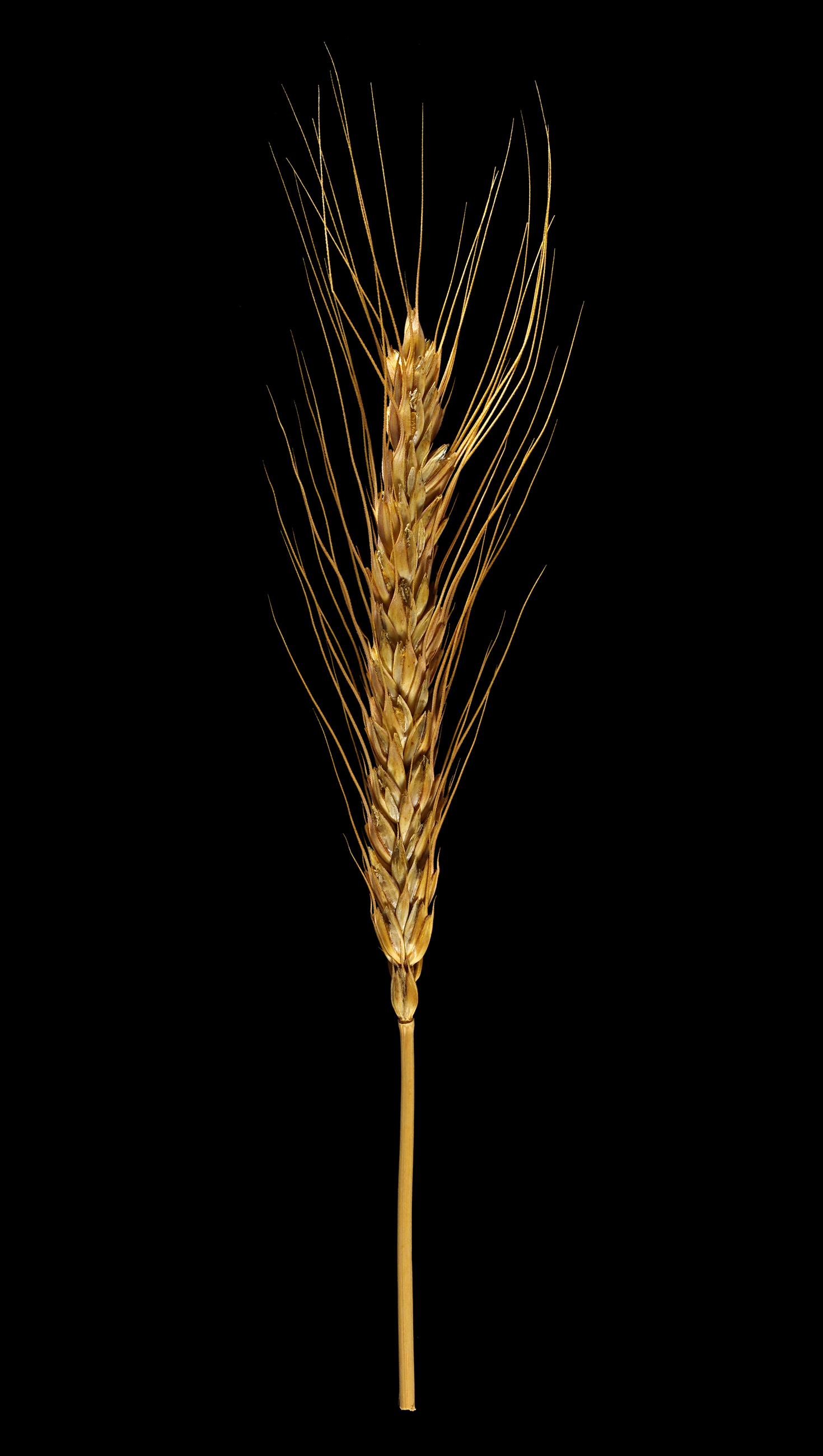
×Secalotricum is a fertile hybrid of male wheat (Triticum) and female rye (Secale). This grain is also described in its baking properties as a mixture of both.
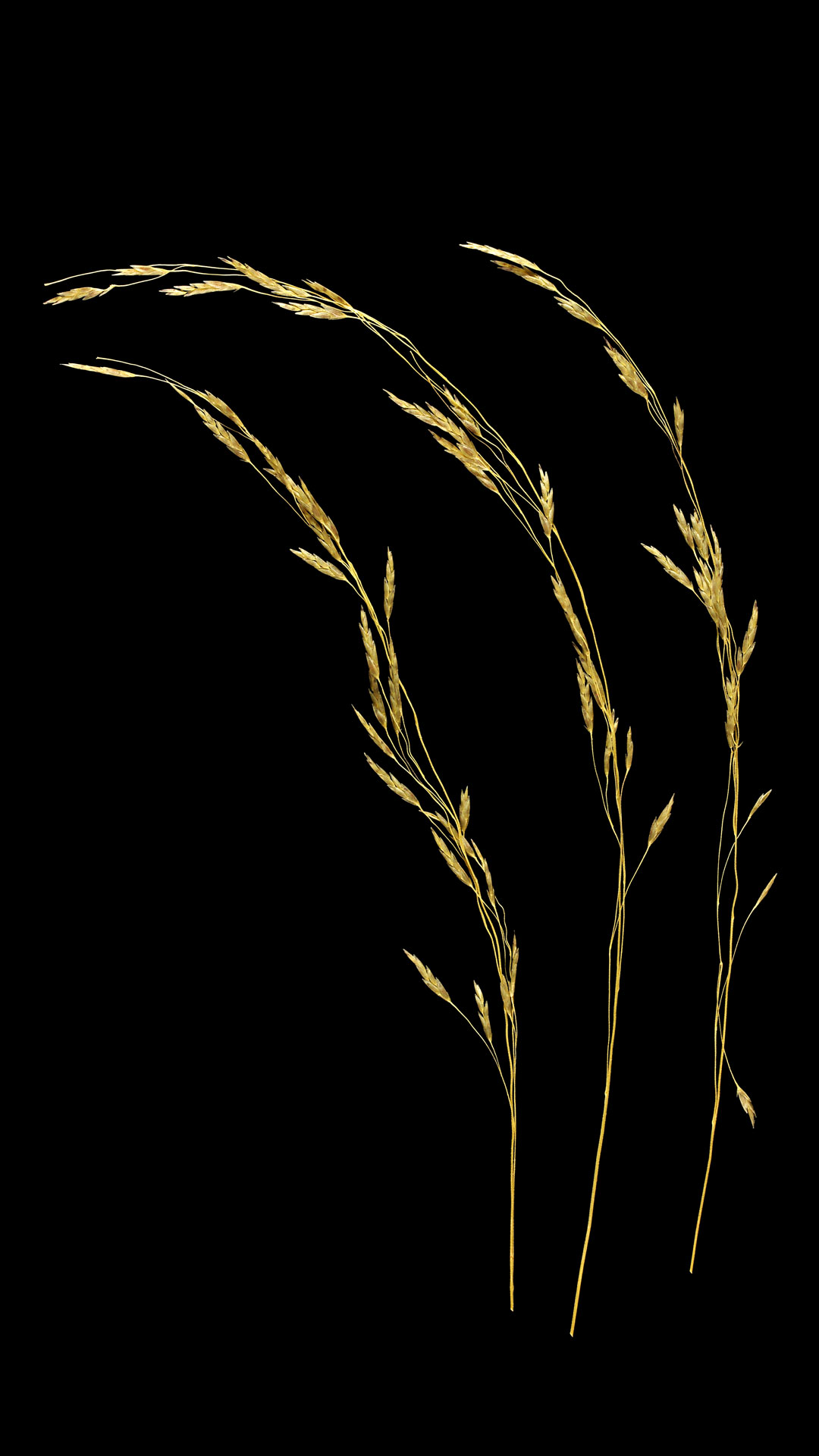
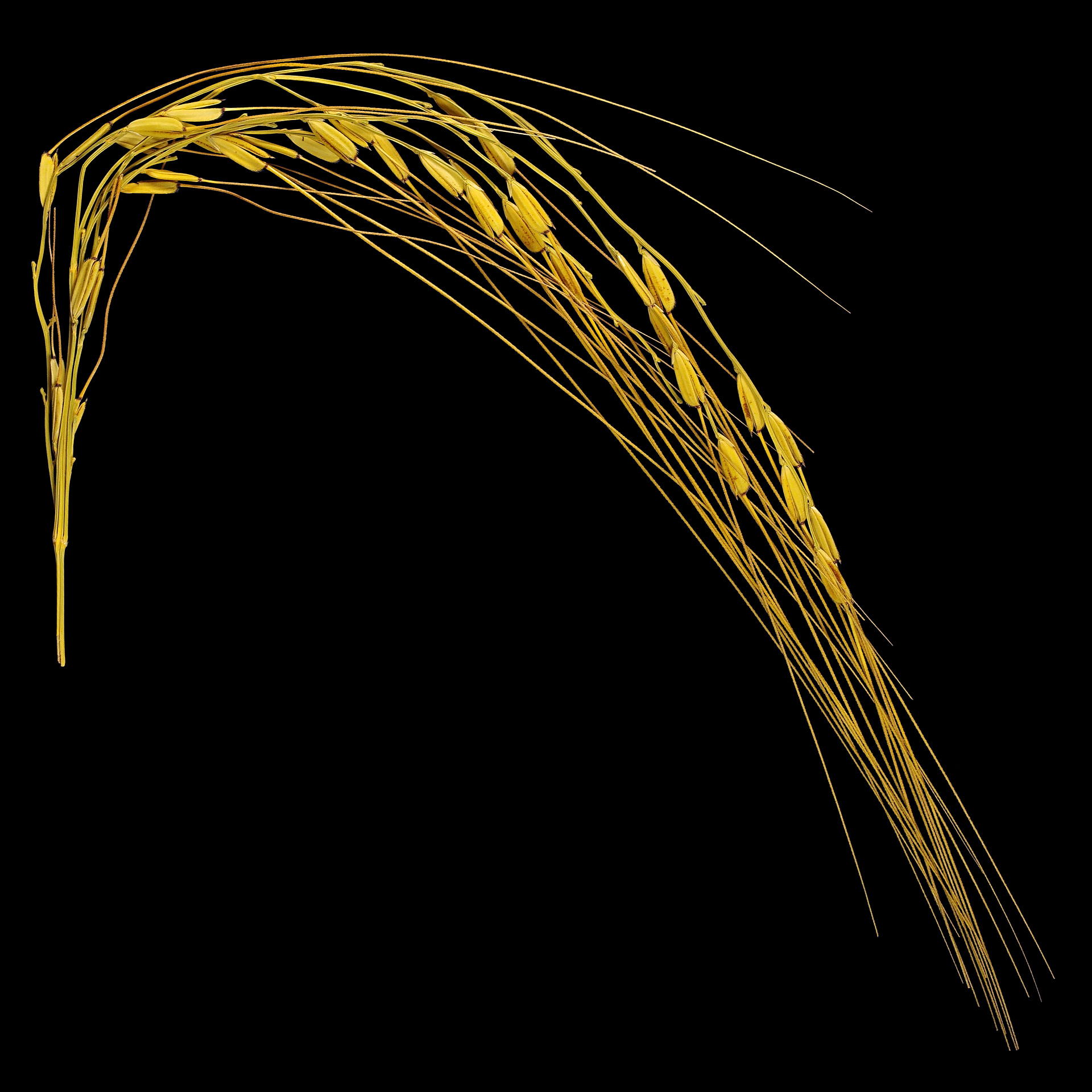
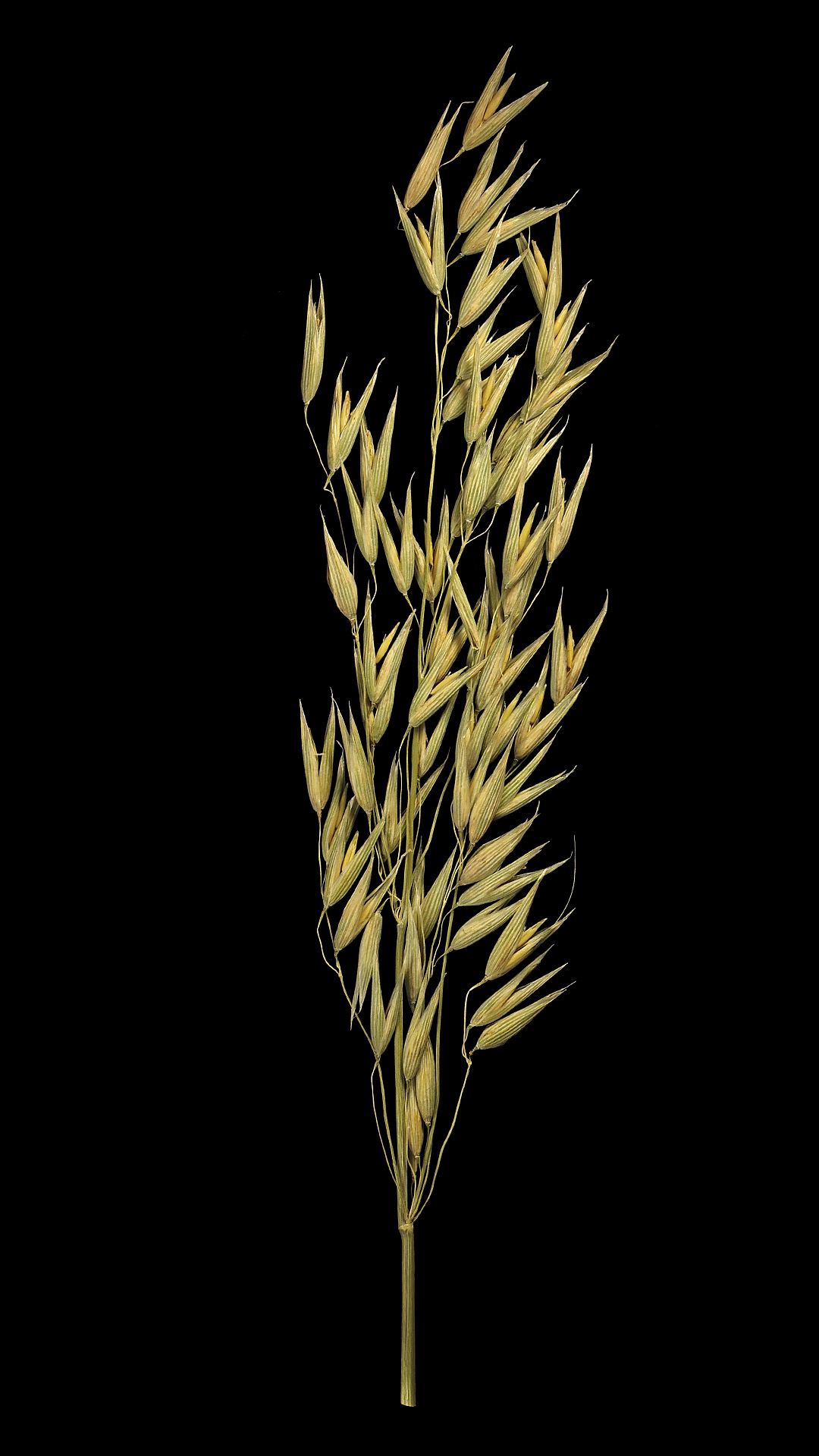
Wild oat is edible and can be valuable in times of need as a famine food.
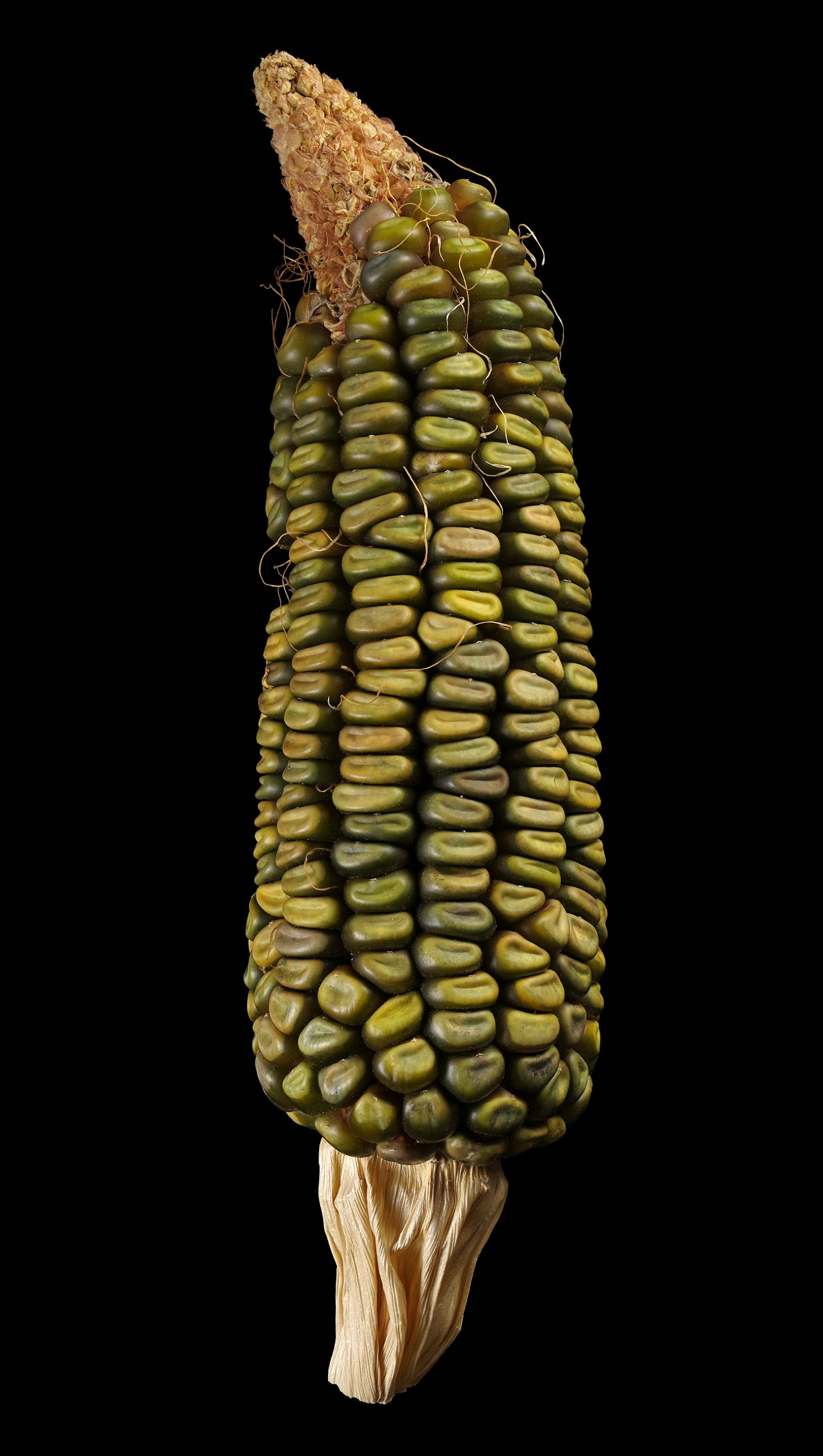
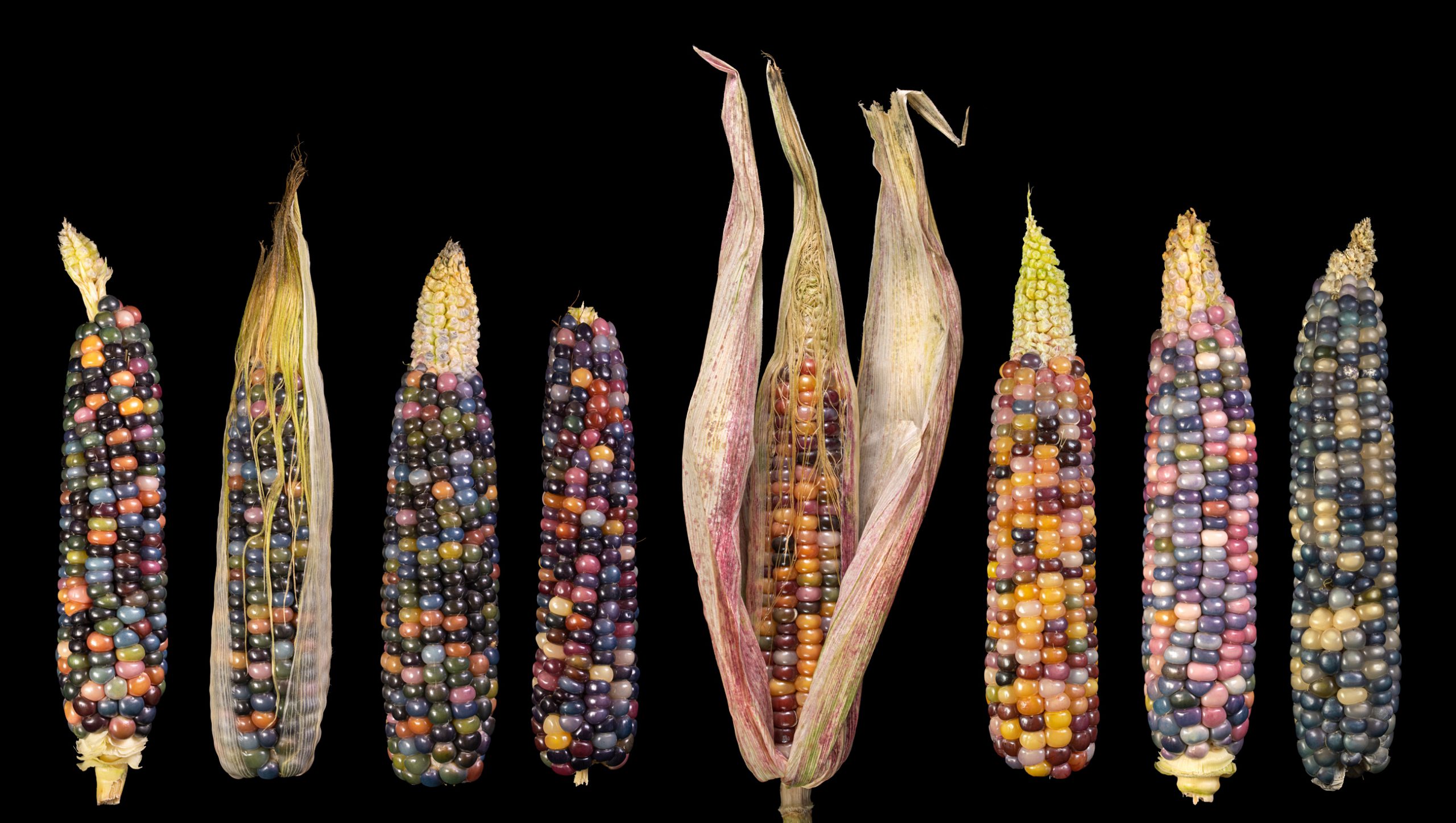
Oaxacan Green dent corn is an old, green maize variety with very large cobs that was cultivated by the Zapotec Indians of Mexico in the province of Oaxaca.
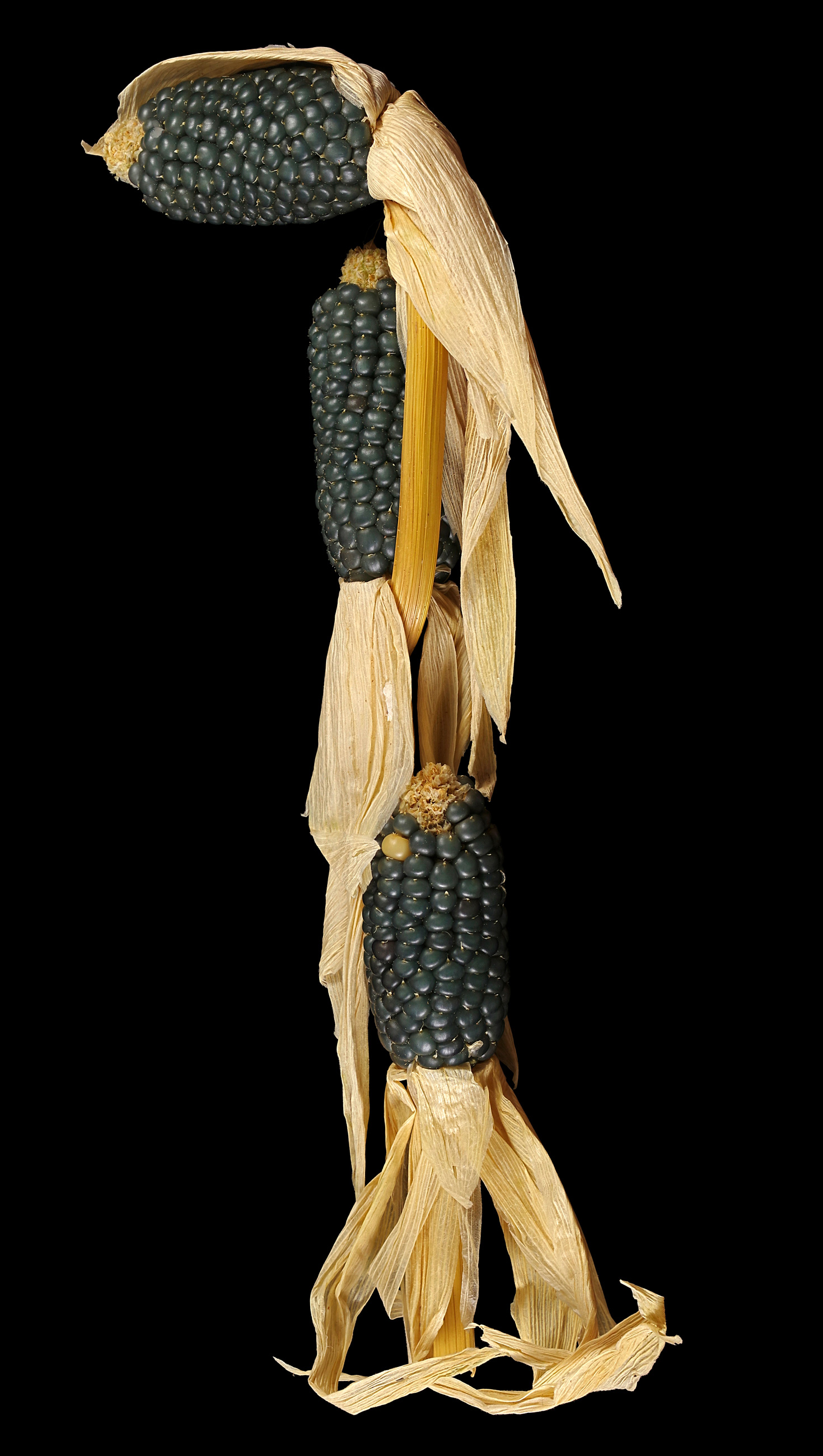
This dark popcorn bears comparatively many small cobs with small, round grains. These are almost black, with a blue-green shimmer.
Although the seeds of the hairy love grass produced in panicles are only about 0,5-0.8 mm in size, they are used as cereals.
The numerous, tiny seeds are collected wildly in times of food scarcity, slightly roasted and ground into a flour from which a thin meal soup or porridge can be prepared.
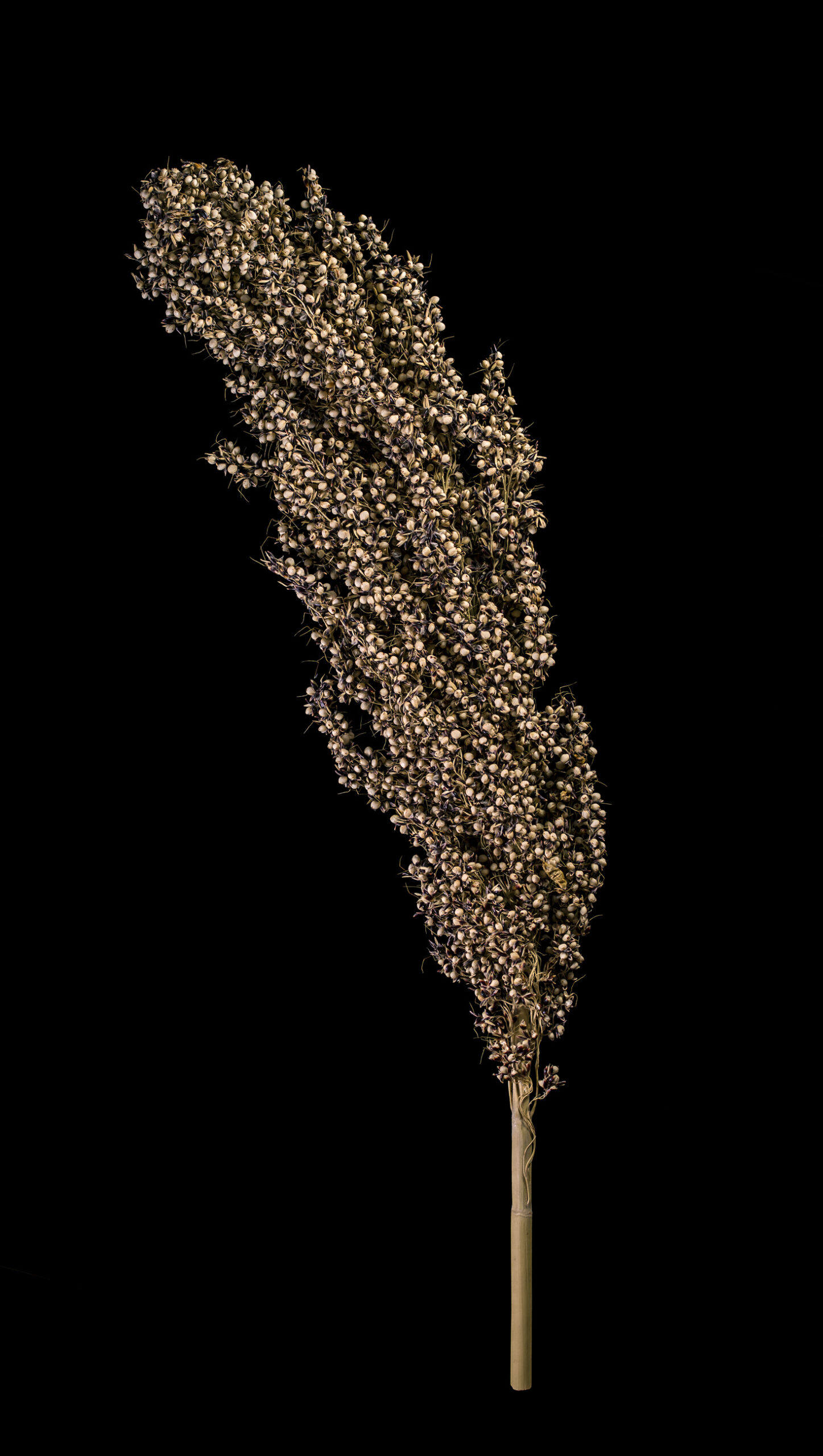
Pearl millet is processed into millet gruel or flour, which is usually eaten as flatbread. Beer can be brewed from this crop.
A mash can be prepared from green rice and it is used as a coating for frying. With sugar, green rice can be cooked to brittle.
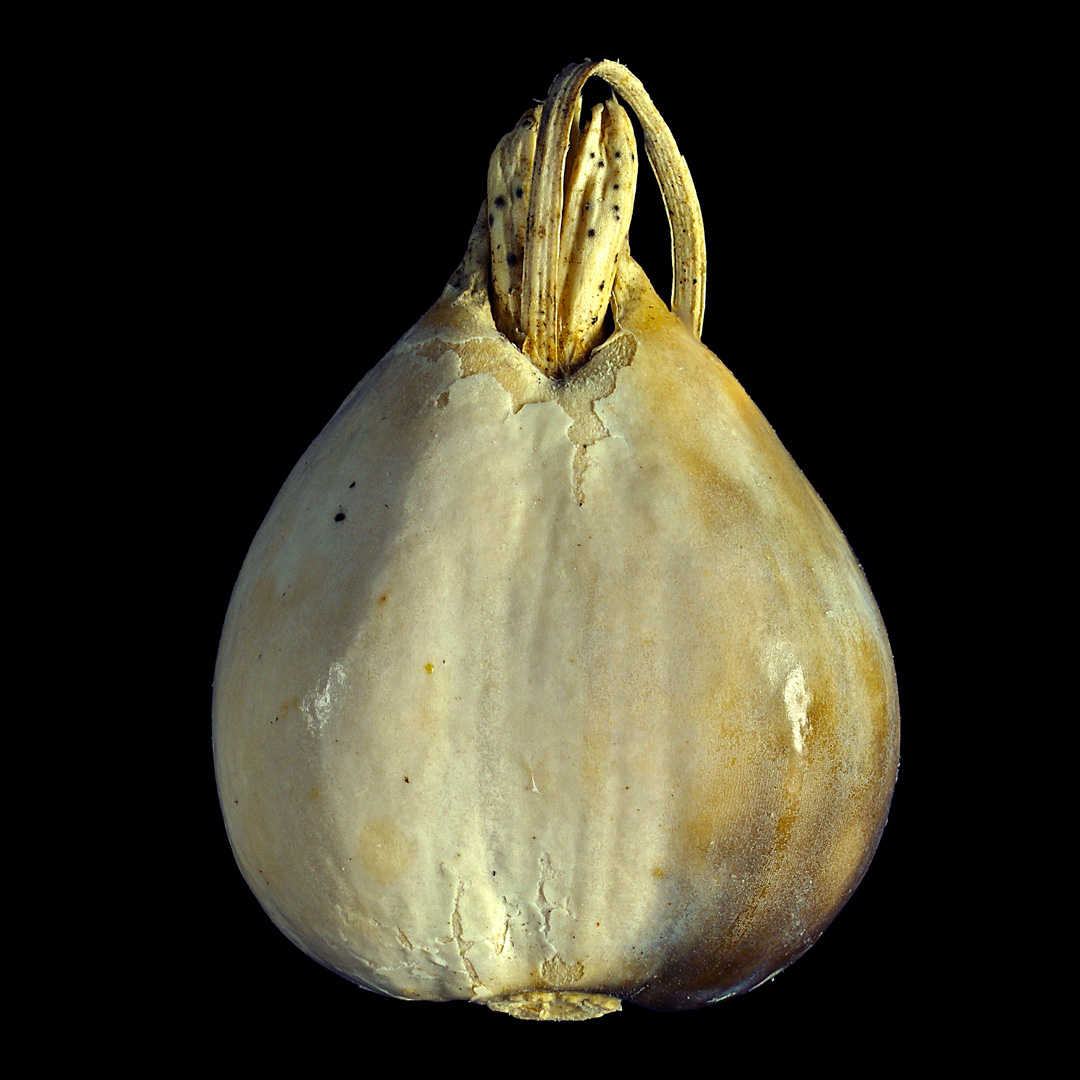
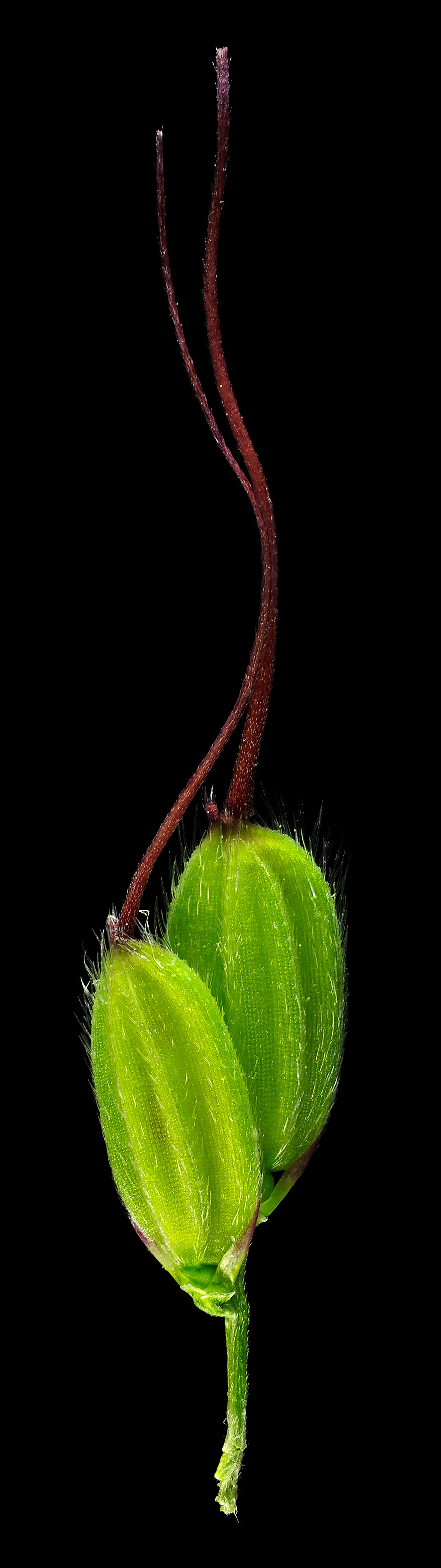
This wild form of african rice is used in times of food scarcity until today and is sometimes even sold as a crop at local markets.
The dried grains can be popped or ground into flour, but flour and popcorn are then no longer so colourful.
In contrast to many other cereals, oats do not need to be peeled, only dehulled. Oats are always a wholemeal product and therefore rich in vitamins, minerals and fibres.
Sorghum is a staple food in parts of Africa (especially West and East Africa) and India.
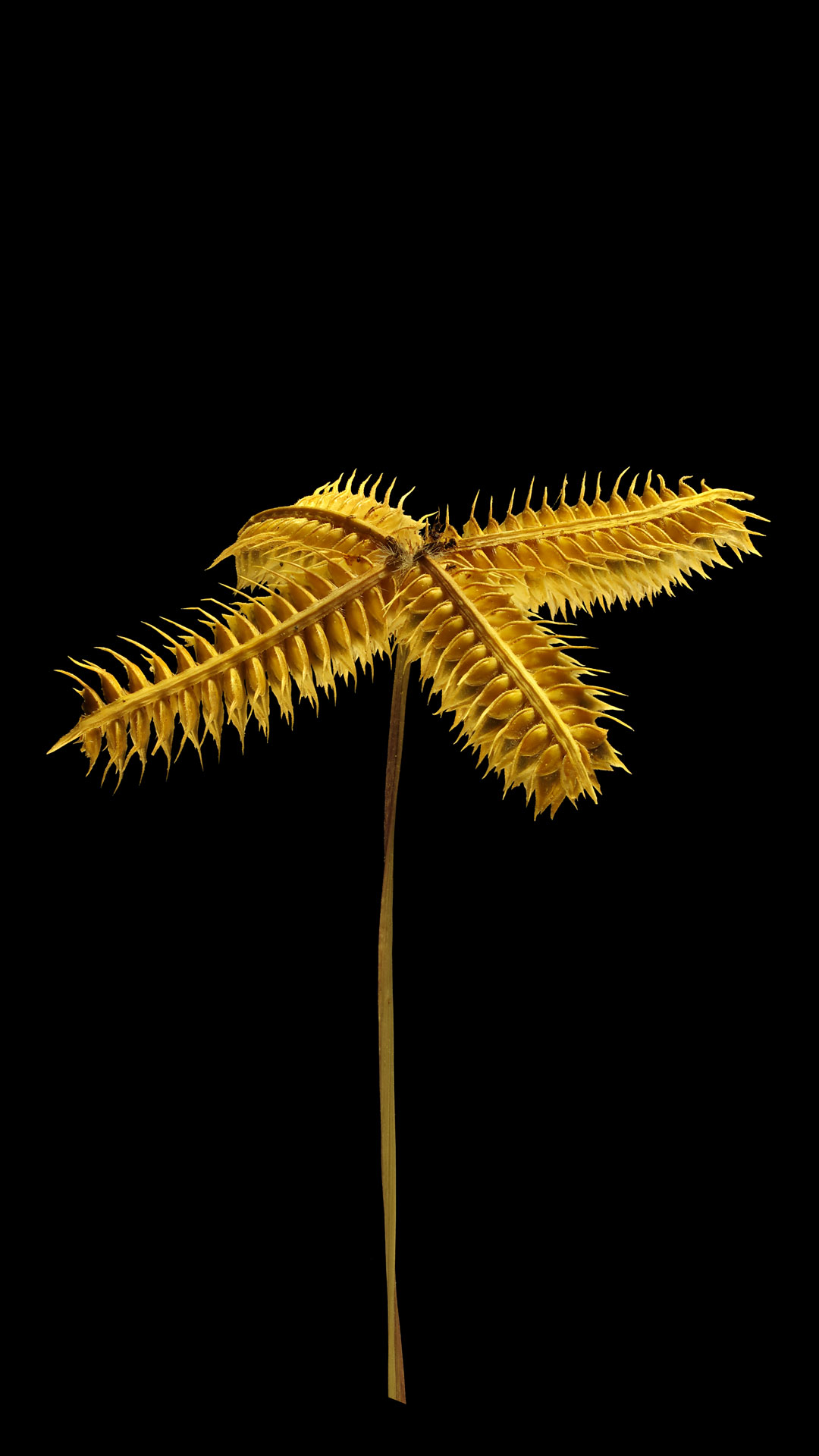
A striking characteristic of T. sinskajae is also the more compact and “round” shape of the awns.